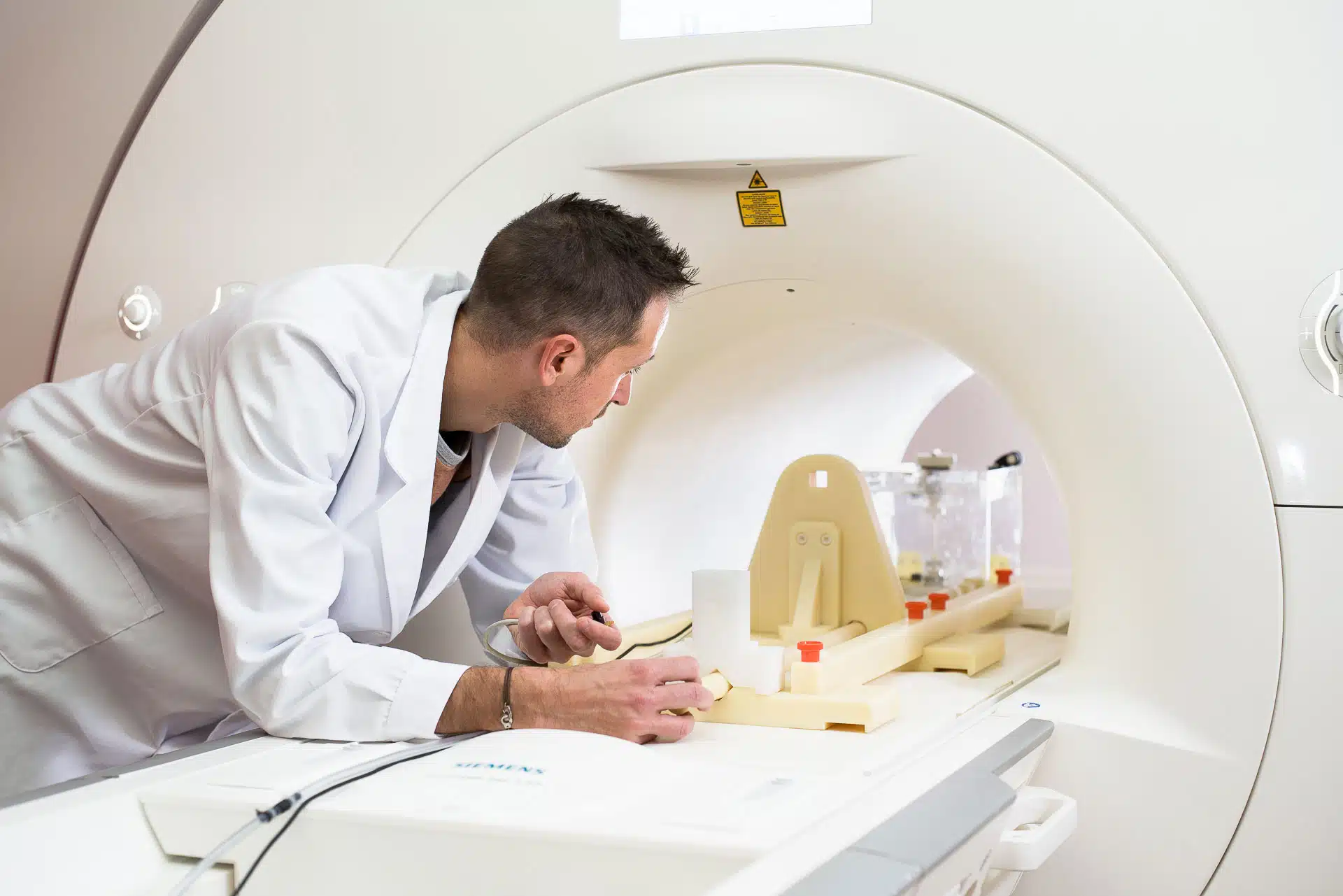
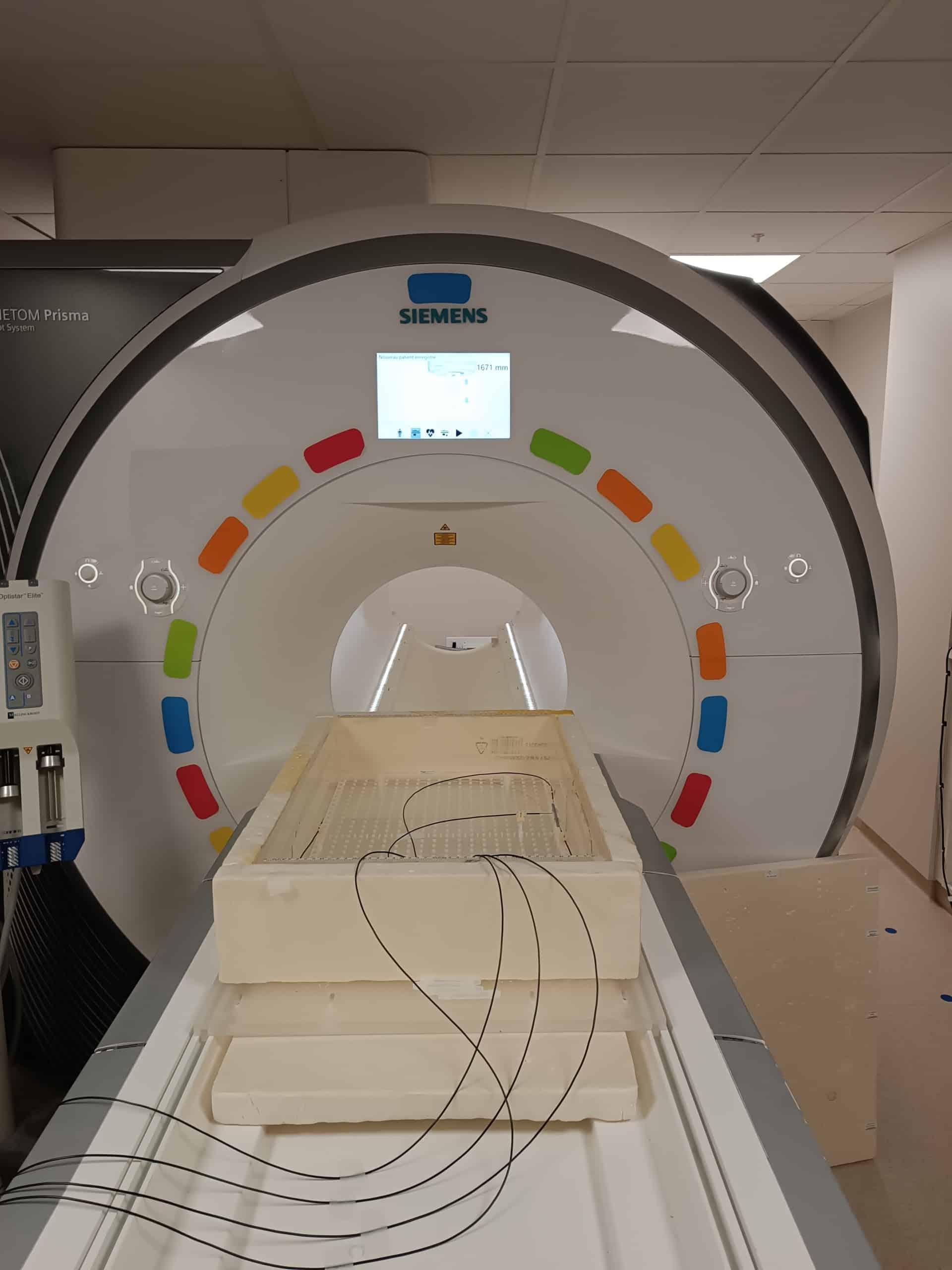
The risk associated with radiofrequency (RF)-induced heating is often the most critical factor when assessing the safety of medical devices in MRI. The ASTM F2182 standard is the reference experimental method for measuring these temperature increases on passive implantable devices (orthopedic prostheses, stents, plates, etc.).
Principle of the ASTM F2182 method
The method can be summarized in four steps:
- The implant is placed inside a phantom (a container filled with a gelled saline solution that reproduces the average electrical and thermal properties of the human body).
- Temperature probes are positioned at potential critical locations (hot spots) to measure temperature rise.
- Measurement of the temperature increase with the implant exposed to RF.
- Reference measurement, without the implant, to characterize the local exposure at the measurement points and to assess the exposure level. The goal is not to directly predict the in vivo temperature, but to evaluate an implant’s tendency to heat under controlled and reproducible conditions.
Limitations of the ASTM F2182 method
- No acceptance criteria are defined; these thresholds must be established by the manufacturer.
- ASTM F2182 does not provide a standardized method for identifying hot spots, which requires either preliminary testing or electromagnetic simulations.The homogeneous medium does not fully reflect the in vivo environment (vascularization, perfusion, bone anchoring, etc.), and additional studies are often necessary to determine the expected in vivo heating.
Conclusion
The ASTM F2182 standard defines the reference method for measuring RF-induced heating of passive implants in MRI. It provides a reproducible method recognized by regulatory authorities. However, it does not define acceptance thresholds or a direct correlation with in vivo conditions. Manufacturers must therefore:
- supplement the analysis with numerical modeling
- establish their own acceptance criteria,
- incorporate the results into the MRI Safety Labeling in accordance with ASTM F2503 and FDA recommendations.
When properly applied, the standard helps determine the conditions under which passive implants do not present an excessive thermal risk during an MRI examination.